Heterogeneous Computing
Hardware Thread-Level Speculation System
Thread-Level Speculation
If you are interested in Parallel Computing, Multi-core Architecture, Cache Consistency Protocol, I hope this page can provide you with what you want to know.
🎯 Vision and Goals
With the increasing complexity of the design of the processor microarchitecture, the space for optimization and improvement is gradually reduced, and at the same time, the progress of the manufacturing process has slowed down, and it is difficult to rely on the process to improve the processor performance. Under such circumstances, the performance of single-core architecture has hit a bottleneck, and according to Amdahl’s law, parallel execution using multi-core architecture is an effective way to further improve program efficiency. Therefore, serial program parallelization is necessary, but the factors affecting parallelization are not easy to be overcome, such as the program itself does not exist parallel parts, or the access control of shared resources after parallelization is too expensive.
Thread-level speculative parallelism is a multi-core parallel architecture, which uses multi-core to accelerate serial execution programs. It divides serial programs into several ordered fragments, runs these ordered fragments on multiple processor cores, processes all fragments according to the out-of-order execution sequence submission. If the fragment execution fails, it is rolled back and resumed until it can be submitted. Keep the program moving forward. The parallel architecture can use locks to control the shared resource access between parallel programs, and its synchronization cost is large, and the locked area is still serial execution, while the thread-level conspeculating parallel architecture as a lock-free parallel architecture can realize the parallel execution of serial programs in the true sense.
At the same time, heterogeneous computing is a hot spot in the current computing architecture evolution trend. Intel’s Alder Lake combines Goldencove and Gracement cores to improve the multi-core performance of processors under limited area resources. Generally speaking, the energy efficiency core is limited by resources, and the single-thread performance is necessarily weaker than the performance core, but the area is small, and multiple energy efficiency cores can be integrated in the same area, providing multi-core advantages. In order to make better use of the multi-core parallel capability of the energy efficient core, increasing the thread-level inference parallel extension will improve the overall performance of the energy efficient core and play its multi-core advantage. Take the size of the Intel 12700 platform as an example,
According to the layout published by Intel, the area of Goldencove core is about 4 times that of Gracement core, and if the use of thread-level inferred parallel to execute serial programs on 4 Gracement cores, the acceleration ratio can be more than 2 times faster than the performance core. Then it would be profitable to add thread-level speculative parallelism to energy efficient cores.
The following focuses on the basic concepts of thread-level speculative parallelism
Thread-Level Speculation (TLS), Also known as Ordered Parallelism, Multi-Versioned Cache, and Multi-Versioned Memory
From the perspective of cache consistency, the distinctive feature of TLS is Multi-Versioned, which, as a parallel technology, focuses on the read and write control of shared resources. This technology can be traced back to 1995, with the hot CMP mentioned at that time, ideally one core has difficult multi-core support, but want to make multi-core use, parallel programming is a problem, common is to lock, rely on the processor to provide atomic operations, but for the user program, the use of these calls is high cost, It is also difficult to write an efficient and correct parallel program, such as deadlock problems. So people are looking for ways to avoid using locks to execute programs in parallel, essentially extending the atomic granularity of an atomic instruction that is limited to the behavior of a single instruction to a single piece of code. Although the use of two atomic instructions can also be achieved, such as the critical section, but the critical section only allows a single thread to execute, which means a waste of multi-core resources, does not meet the original appeal of maximizing the use of multi-core resources.
In short, whether a program can execute in parallel depends on whether there are conflicts in resources, such as shared variables, if there are multiple simultaneous reads, multiple simultaneous writes regardless of the order, but multiple sequential writes (such as memory consistency, program order, etc.), there is the possibility of violating the program order. Therefore, to solve this complex scenario, Thread-Level Speculation is proposed, which requires the resource conflict between parallel programs to be solved during runtime. If the problem is narrowed, the shared resource mainly refers to the memory block, and the conflict is that the load/store operation does not meet the behavioral requirements of the program, such as: For loop N times, now there are N cores, let N iterations run directly on N cores at the same time, if there is a load/store operation of the same memory block between iterations, then it is possible to error (iteration i < j, Store j occurs before Load i). This example covers some of the key issues in implementing TLS technology:
- How to check for errors
- How to recover
About more technical content is not expanded here, I believe that here, you have a rough understanding of the thread level speculation parallel to achieve what purpose, more content can be in-depth understanding in the follow-up process, such as:
- Hardware/Software TLS
- Connection between Transactional Memory and TLS in practical applications
- Eager/Lazy conflict detection, eager/lazy versioning, lazy commit
- False sharing, privatilization, word detection
- Spwan programming model, what/why?
- Software/Hardware rollback
- The relationship between task splitting, cold start, page missing exception, and programming model’s auxiliary performance improvement for hardware design
⛳️ Overview
In the past year, the thread level speculation parallel system has been built on the Gem5 platform, which supports:
- OoO CPU
- Cache Coherency Design
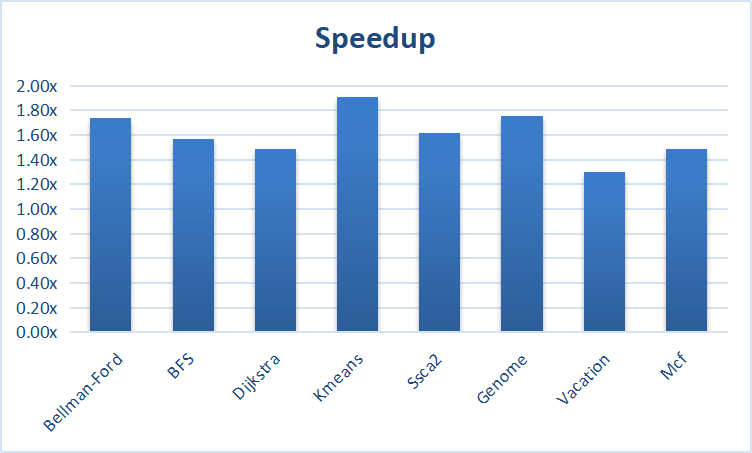
Currently in the stage of finding Benchmark:
- SPEC2006, excluding lbm, libquantum, milc, h264ref, sphinx3, their program behavior is inappropriate, are parallel, but part of the compiler static period is not analyzed (there are Pointers and other influencing factors), mcf can consider modifying it
- Olden Benchmark, this is to measure transaction access, but no harm, it can also be used
- STAMP, also transaction access, has been modified with kmeans, and the effect is ideal
- Graph benchmark, which is currently written by two algorithms, Bellman-Ford and BFS, is not very satisfactory. The problem is that the programming model is not working well, and there is a large room for improvement in program tuning
⭐️ Common documents and links
💡 Knowledge base help
Published on